Expert Diabetic Child Care System 1
1997/07/01 Sierra, Basilio | Remiro, Arantxa | Pikaza, Juan Manuel Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria

Diabetes is the most widespread chronic disease among children and in the developed world. His life is complete and therefore, if he is not cared for carefully, he carries a high risk of serious problems (blindness, legs or amputation, etc. ). When it is said that it is necessary to take good care of it, therefore, the gravity of these problems is taken into account.
Diabetic children must be taught from a young age that the whole responsibility of their body is theirs and that others, at most, give advice. Your responsibility will always be to take into account the factors to consider in this care process: blood sugar level, diet, sport or insulin dose, among others.
Doctors need each and every patient data to decide how to act with the disease and to explain to children what exactly they should do. A lot of data needs to be taken into account and in general it takes time to see them well. Every day we have to make 3 data collected on average and in each data collection we can analyze 14 different values (blood glucose, insulin, food, sport, ketonuria, day, time, etc. ). Every 4 months go to the doctor with all the data you have collected.
Analyzing the characteristics of this disease, the possibility of using an Expert System can be a good solution. We will call the Expert System the program capable of understanding, explaining and learning. In the case we have studied, the goal of the system is for children to know whether or not to properly care for the disease.
The work described below has been aimed at facilitating the work of the doctor and for this we have used Artificial Intelligence techniques. The first step we took was to make a device to collect patient data. We then carry out a program of reading this data, in which the information is stored in a database, which finally allows to relate the information that is collected from the database with the data of the patient himself and obtain an explanation.
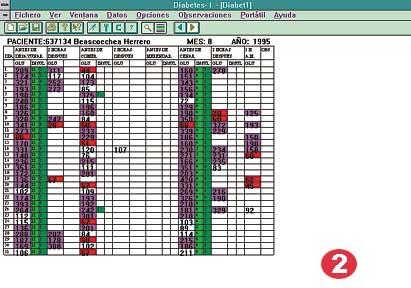
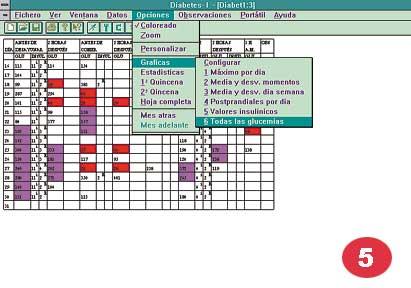
The program is prepared for the Windows environment, so it is very useful and we can provide data in a very representative way. The data are shown in figures, but special data such as hyper and hypoglycemia can also be shown in color. In addition to those already mentioned, the system can provide more graphic and statistical resources and, finally, the possibilities offered by the Expert System itself, the organization of this data in medical reports, among others.
What is the Expert System?
Expert System (SA) is a computer program that mimics expert responses. It is located in the branch of Artificial Intelligence in Informatics and since the 70's they have been used a lot, especially in medicine. One of the main characteristics of the SA, and its most evident difference with common programs, is the management of uncertainty, that is, that the program outputs are not fully detailed, but are given with a level of confinement. Usually the confidence level is the probability of the decision. The most prestigious system is the MICYN expert, as it provides the diagnosis of contagious blood diseases as well as the best experts in the world. It was made at Stanford University in the USA (California) and, understandably, is a star of the SA. The program we have worked on is the specialization of SA, Decission Support System.
If we look at the Elhuyar Encyclopedic Dictionary, the definition of sweet diabetes is as follows:
“Metabolic disease that increases the glycemic level of the blood. It is very normal. The pancreas is unable to synthesize enough insulin to control sugar metabolism. Consequently, the blood sugar level exceeds normal values. Its origin may be in a pancreatic lesion or other diseases. Treatment using insulin vaccines.”
Being chronic, patients should know how to maintain sugar levels in acceptable values, controlling their body throughout life. To do this, three main factors must be under control at all times: diet, sport and insulin level.
A person with diabetes has to eat healthy, daily meal measures should be varied and balanced, should perform physical exercise properly to avoid an excessive decrease in sugar levels and take without excuse the insulin doses indicated by doctors in the hours prescribed by doctors.
Insulin delivery times are usually two, three, or four times a day. The prescribed schedule follows a certain pattern, which is why it is called a guideline; for example, the most used guideline is usually “before breakfast and dinner” in cases where the patient should take insulin twice a day.
Computer Medicine
Since the use of computers was completely extended, the resources offered by computer science are widely used in medicine, since computers facilitate the control of many data in medical centers. Currently, the needs of people working in the health sector are as follows from the point of view of the Healthcare Information and Management System Society:
- Use of computer networks (internet, email...)
- Database consultation (for doctors)
- Share digitized patient information
- Data collection and processing
- Integration of different resources
The organization of information is very important, taking into account the hospital information systems, the computer registry of patients, clinical images, telemedicine, security, etc.
The computer registration of the patient, for example, is a European project that aims to introduce all the data of a patient into a magnetic card. The project includes reading this card in any European hospital center and its main applications are diagnosis, telecontsultation and organization of treatments.
As mentioned above, one of the main fields of Artificial Intelligence is medicine, since for this purpose the most prestigious expert systems and many other instruments have been designed. The design of an expert system involves the consolidation of the area of knowledge of the doctor, which can be done by rules and which currently use other more sophisticated techniques such as machine learning.
On the other hand, mathematical models are used to measure the behavior of the patient and convert the decisions of doctors into models in each specific case. Most models are statistical, including logistic regression, discriminant analysis, Dempstes-Shafer theory, causal models, dark logic, neural networks, Bayesian networks, etc. are the most used.

The Auxiliary Decision-making Systems are part of the subset of Expert Systems, which aims to support health professionals and increase the performance of clinical equipment, improving the diagnostic process (what to ask, what type of tests and what process to follow, among others), facilitating treatment, helping to design the experiments and carrying out the management and tutelage of hospital resources.
Project DIABETES I
Our main objective is to facilitate the work of the doctor and the patient.
As already mentioned, diabetes is a lifelong disease and patients have to be vaccinated several times a day, writing in a notebook the levels of glycemia, insulin introduced and other data on sport, food or other factors that influence the disease and going every three months to doctors to inform them of everything. The doctor, through the review of this data, can know the exact status of the disease and determine whether the insulin dose should be modified or should undergo a new pattern.
The objective of this system is to facilitate this work and for this we have developed an electronic device, similar to a calculator, that allows the patient to enter encoded data that must be taken into account.
Interface
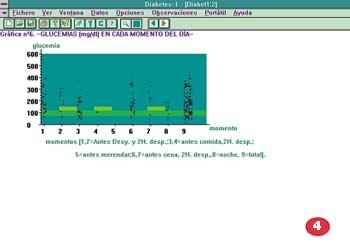
In order to facilitate the user's work, a Windows-based program has been developed that allows you to read and view all this data from that electronic device easily, including graphics of different options, statistics and data of the day. To perform this program we used Visual C++. It is an interactive system that can be run on any PC, if the patient has a computer it is given a small part of the program.
Expert Systems
Among the options offered by the program is the Expert System. This allows the doctor to see more quickly the behavior of the patient and the measures to be taken from the data, but keep in mind that the criteria collected by the Expert System (in our case the Auxiliary Decision-making System) are only recommendations and that the final decision must be made by the doctor himself.
We have had the collaboration of a team of doctors for the elaboration of the Auxiliary System of Decision Making who have worked decisively in the implementation and interpretation of the decisions they have to make in the day to day. Thus, we can say that our program follows the behavior of a medical team, that is, the advice given by the system are those that doctors themselves give us. Logically, the use of the rules must be done with uncertainty, as in all Expert Systems.
Below is an example rule taken from MYCIN:
If
the blood color is NEGATIVE GRAMM and is known and the patient is in danger,
then PSEUDOMONAS (0.6)
This rule is 60% reliable.
Statistical techniques are used to manage uncertainty and conclusions are obtained using probabilities. In our case, doctors have told us the uncertainty of the rules and the use of them.
The set of rules is a knowledge base that, so to speak, simulates the knowledge of doctors. The process for obtaining this knowledge is called knowledge engineering; in expert systems it is totally normal that this work is necessary, although at present there are other techniques that allow machine learning from data such as the opening of a Bayesian Network (Expert Probabilistic System).
Database
The most important part of this work is the inclusion of all data in an Access database from which we obtain a medical report. The ODBC ( Open Data Base Connectivity) has been used to connect the program and Access. This report presents a summary of patient data, their behavior during this trimester, data consistency with blood test data (such as glycosylated hemoglobin) and system conclusions. We have conducted macro rule simulations in Access to make doctor decisions.
All data obtained from the electronic device in the database are associated with the patient through relationships and the data from the blood analysis are integrated into the database (at the moment manually) by the doctors so that the program collects them in the report. This use of the program is not left in the hands of patients, since for them it is difficult to obtain these blood data.
CONCLUSIONS
This project has led to the creation and consolidation of a multidisciplinary team, providing a practical solution to a real problem.
On the one hand, the computer team has experimented with different techniques and tools to apply the most interesting techniques of computer science and artificial intelligence. On the other hand, the medical team has structured the knowledge of this field through a debate, obtaining a knowledge base. You have entered all patient data in the database indicating the steps to follow for your control.
The tools used are:
Hardware:
Personal computers
Data collection device.
Software:
Microsoft Visual C++ (To perform programs)
Microsoft Access (Database)
Open Data Base Connectivity (To link database and programs)
Dynamic Data Exchange (To perform database tasks directly)* Faculty of Computer Science of Donostia. UPV/EHU

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia




