Protective cover for protective cover
2005/06/01 Galarraga Aiestaran, Ana - Elhuyar Zientzia Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria

M M
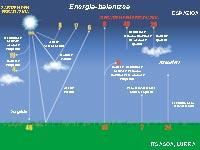
The whole emits electromagnetic radiation of all wavelengths, but not all reach the terrestrial surface. Most of the high-energy radiation is clogged in the upper layers of the atmosphere. There, the molecules are divided and the atoms lose some of their electrons, thus becoming ions. Thus, above 80 km, the atmosphere has numerous free ions and electrons. This part of the atmosphere is called ionosphere.
Below, at a height of 20-25 km, is the ozone layer that prevents short-wave radiation from reaching the terrestrial surface, the ultraviolet rays. Its effects are known to dermatologists, who cause cancer and severe burns in the human skin. Less evil than almost everything stops!
Even though the ozone layer is really protective and effective, do not think it is a thick cover: if the earth surface was subjected to atmospheric pressure, it would only have a thickness of three millimeters. However, if it disappeared, the Sun, our life-giving, would become mortal.

Ozone is formed by three oxygen atoms that are formed thanks to ultraviolet radiation. In fact, at the top of the atmosphere the ultraviolet light divides the oxygen molecule, leaving two free oxygen atoms. When one of them passes into the stratosphere and binds to an oxygen molecule, the ozone molecule is formed. Sometimes, the oxygen atom binds to a molecule of nitrogen forming nitrous oxide.
On the other hand, when ultraviolet light meets ozone, it divides the ozone molecule into a new oxygen molecule and an oxygen atom. Ozone is, therefore, a constant cycle of formation and destruction.
The hole needs patch
However, the ozone cycle is easily cut by chlorine, fluorine, or atomic bromine. These elements are found in several stable compounds, mainly chlorofluorocarbons (CFC). If CFCs reach the stratosphere, ultraviolet rays divide them and atoms are free. A single chlorine atom is capable of breaking 100,000 ozone molecules.
We must also take into account the supersonic planes, which shed nitrous oxide and water. When flying in the lower part of the stratosphere, they are very harmful to the ozone layer.
Otherwise, the concentration of ozone varies greatly with the latitude, thicker in the equator and thinner in the poles. Researchers estimate that the concentration of ozone in the northern hemisphere is decreasing by 4% annually. Likewise, approximately 4.6% of the terrestrial surface lacks ozone layer, which are the holes of the ozone layer. This means that in these places there is no shield that protects from ultraviolet radiation.
Scientists have long warned about the possible impact of the loss of the ozone layer. The decrease in the density of the ozone layer by 1% appears to be an increase of 3% in the probability of developing skin cancer. To avoid risk, governments have already begun to take steps to prevent the destruction of the layer. The first were the Swedes, which in 1978 banned aerosols that damage the ozone layer.

Despite the subsequent opening of international measures, the concern has not disappeared: In August 2003, the US Geophysical Association He reported that the loss of certero ozone was slowing down, while the hole over Antarctica was the second largest of all time. In addition, they have now seen that the ozone layer on the Arctic has been thinner than ever in the winter spring of this year.
While it is true that the prohibition of CFCs has been favorable, it should not be forgotten that the ozone layer is also influenced by other substances used by man, such as methane, nitrous oxides, sulfate particles, etc. Therefore, researchers will continue to watch over the thickness of the layer to avoid excessive thinning.
Warm warm and warm
In any case, protection against radiations is nothing more than a benefit for the atmosphere. As Fernando Mijangos of the Department of Physical Chemistry of the UPV says, “the atmosphere is the blanket of the Earth, without it the average temperature of the planet would be -18 °C”.
The greenhouse effect of the atmosphere must have an average temperature of 15ºC and that the temperature changes between night and day are not excessive. It is striking that in the atmosphere there are hardly any other gases, besides nitrogen and oxygen, and yet some of these gases that are at low concentrations are responsible for the greenhouse effect.
From a biological point of view, oxygen and nitrogen are essential: they take advantage of oxygen to oxidize nutrients, obtaining energy and nitrogen is fundamental for the production of amino acids. But neither of them is responsible for the temperature of the planet. The molecules formed by two atoms do not affect the greenhouse effect, but the greenhouse effect is formed by three or more atoms.
In fact, the main cause of the greenhouse effect is carbon dioxide, which is due to approximately 60% of the total. It is followed by methane, with approximately 20%, followed by CFCs with 14%. Finally, nitric oxide generates 6%.
Carbon dioxide and others work as greenhouse crystals. Although part of the energy from the sun is absorbed in the high layers of the atmosphere, most of it reaches the terrestrial surface. The Earth itself absorbs part of the radiation and the rest reflects it in an infrared form. However, these gases act as mirrors and return the heat to the terrestrial surface. Therefore, the temperature of the planet increases.
From cotton cover to synthetic
However, in recent times the concentration of these gases in the atmosphere is increasing due to human activity. At the beginning of the industrial revolution, the concentration of carbon dioxide was 280 ppm. However, at present it exceeds 350 ppm. Most of the carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere are produced by the burning of fossil fuels and another part by deforestation. CFCs are still used in numerous industrial activities, methane is generated in anaerobic processes and nitrous oxide in combustion and in the degradation of fertilizers.

By increasing each of them, in addition, other processes are reinforced and, finally, the impact is exponential. For example, when carbon dioxide increases in the atmosphere, the temperature increases, so the air can take more water than before. In addition, more water is evaporated from the sea. And the water vapor itself also contributes to the greenhouse effect.
On the other hand, it must be taken into account that the sea absorbs a lot of carbon dioxide, but an increase in temperature would reduce the dissolution of gases, which would increase the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
However, it is not predictable what will happen, since all processes are interrelated. For example, the union of water vapor molecules will cause clouds that will hinder the energy of the Sun, so it is possible that clouds will help to cool the Earth a little.

However, undoubtedly, the increase in the greenhouse effect will influence. And, according to many researchers, if the trend does not change, the consequences will be harmful. Mijangos again uses the comparison of the blanket to warn of the possible consequences of these changes: “The lids made of new materials heat more than the classic ones of cotton, so at first they are taken to taste, but then we realize that they provide a lot of heat.”
To what extent do the changes that are occurring concern us? Experts do not agree on the conclusions or forecasts, but the vast majority are concerned and believe that steps must be taken to restore the situation before it is too late. But it not only depends on experts.
Shield against the meteors
Besides being a powerful filter and a good lid, the atmosphere is a hard shield. Look at the full moon of holes and craters! The Moon is not protected against the materials that arrive from space. For the Earth would have that aspect if it did not have the umbrella of the atmosphere.
Every day hundreds of tons of material enter the atmosphere. Almost all are small particles, of few milligrams. Its entrance to the atmosphere is extremely fast, at a speed of 40 km/s or higher. At this speed the particles are heated and emit light as they are dissolved. They are called shooting stars.


Not all have the same brightness, the higher the brightness. The bigger ones are called balls or balls of fire and are spectacular, not only for their brightness, but because they allow to see how they get rid. Sometimes the sound they emit when exploding reaches the terrestrial surface and you can hear a kind of buzz. The footprint of the path you travel in the sky can last several minutes.
However, the atmosphere does not protect from all particles. The rocks of several tens of meters of diameter also get rid when crossing the atmosphere, but the larger ones get to the ground. They are meteors and depending on their size can cause appreciable damage in the fall zone.
And it is that the speed brought by the meteors is not negligible and they release a huge energy. Tell us: An object of 35 meters of diameter would release approximately the energy equivalent to the sum of 65 explosives as the bomb that destroyed Hiroshima, a nuclear bomb of several megatons.
Fortunately, they do not fall every day. An object of 10 meters of diameter is estimated to produce a tenth of energy from a megaton that enters the atmosphere every ten years. As it is exploited in the atmosphere itself, it produces no damage. The objects of a kilometer of diameter release energy of one hundred thousand megawatts and touch the Earth every one hundred thousand years. The ten kilometers of diameter fall every one hundred million years and their influence is terrible.
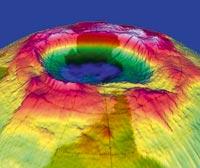
It seems that dinosaurs disappeared 65 million years ago because of a meteorite of these characteristics. Some may discuss the influence of the meteorite on the disappearance of dinosaurs, but there is no doubt where it fell: Created in Chicxulube, Mexico, the crater is 180 kilometers in diameter and almost 50 kilometers deep. Less bad than meteors with atmospheric drilling capacity are so rare!
Upstairs angel, down demon
It is curious that above, in the stratosphere, the same molecule that benefits so much is poisonous here, in the troposphere. Yes, ozone is a harmful contaminant in the lower part of the atmosphere that causes serious damage to human health and plants.
Ozone is not emitted into the atmosphere like other pollutants, there are no sources of ozone pollutants. Although part of the ozone present in the troposphere is produced by natural agents, most of it comes from reactions of chemical substances emitted as a result of human activity. As these reactions are driven by sunlight, the concentration of ozone is higher in spring and summer than in other seasons of the year.
In large cities, it is not uncommon for authorities to warn the public that the concentration of ozone has reached dangerous levels. In these cases, they recommend being inside and not performing physical exercise abroad, adopting measures to reduce the traffic and emissions of the industry.
Ozone causes problems and irritation of the respiratory system in man, among others. But its influence on plants is not sweeter: it damages cells, dampens photosynthesis and prevents the growth of the plant. The persistence of ozone contamination causes losses in agriculture. The most sensitive plants are herbaceous plants, then the leafy ones and the hardest the conifers.