The Meteosat of Meteosat of Second Generation
2002/08/27 Galarraga Aiestaran, Ana - Elhuyar Zientzia
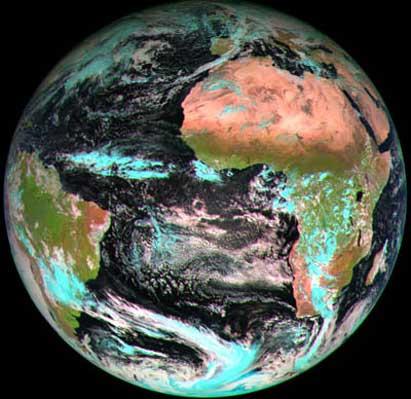
The new satellite is located 36,000 km from Earth in a stable orbit. Located on the Gulf of Guinea in Africa, it will provide 20 times more information than meteorological satellites currently in operation. With this, the weather predictions are expected to be more accurate, but it will also allow for exhaustive weather studies.

The main mission of the MSG satellite is to provide images of your field of view. In this way, these images will allow to analyze the characteristics and thermodynamics of the air masses, as well as the physical parameters of the clouds. In addition, you will see how clouds form and allow you to quickly detect changes. On the other hand, it will collect oceanographic and geophysical data and facilitate them in real time. In this way, these data will be archived and used in different applications.
The data transmission will be carried out through two channels: HRIT (High Rate Information Transmission) and LRIT (Low Rate Information Transmission). Through the first one, all the data of the processed images will be sent compressed, while through the second one only a part of the processed images will be sent, but other meteorological data will also be sent. Both transmission paths will use the same radiofrequencies as the current Meteosat system, but the code, modulation, speed and format will be different.
Another function of the MSG will be to measure radiation. It will provide accurately reflected solar radiation and thermal radiation emitted at the top of the atmosphere. On the other hand, in case of need, the satellite will collaborate in different salvages.
In the coming years, two new MSG satellites will be launched, with a total budget of 1,337 million euros.
To find out more click here

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia