Chemistry of Rocks
2006/05/01 Kortabitarte Egiguren, Irati - Elhuyar Zientzia Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria

Precious stones, in general, are valued for their beauty and perfection. They are perfect crystals, so to speak in some way. Its appearance is very important in these precious stones and its beauty should be, of course, sustainable. That is, they cannot be easily destroyed. If not, they lose their value immediately.
They are divided into two large groups: jewelry and semi-jewels. Diamond, ruby, sapphire and emerald are the jewels of precious stones. Amethyst, jade and others, semiprecious. The difference between both groups occurs mainly in abundance.
Jewelry jewelry jewelry jewelry jewelry jewelry jewelry
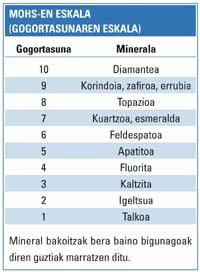
Today the diamond is the most precious jewel. Its hardness is impressive, with a value of ten on the Mohs scale. It is a pure carbon, but the arrangement of these carbon atoms is special and therefore the diamond is so hard. It also has a special shine, which surprises anyone. In fact, it has a high refractive index of light and a huge dispersion capacity of it.
In India, Brazil and South Africa, for example, there are many diamonds. However, the characteristics of the ground are not the same everywhere, and thus neither are the extraction of the diamond. In general, three main steps are taken. First, remove the lands and stones that cover the diamond, then extract the diamond and finally clean it properly.
It is a very laborious work. For every ten tons of mineral, only one kilate of diamonds (200 mg) is extracted. From there take the accounts. There are many kilometers of earth that need to be excavated to get a jewel of medium size. Precisely that is why the diamond is so expensive.
But don't think all diamonds are useful for jewelry. The most diminutive error can reduce its value, so it can be used only for industrial applications. In general, this happens in the case of diamonds with bubbles or impurities. In the industry they are used to cut metals such as diamonds.
On the Mohs scale the blonde has a degree less than the diamond, that is, red precious stones formed by combinations of iron, chromium and aluminum oxide. Among them are Myanmar, Sri Lanka, India, Thailand, China and Russia.
However, they are not only natural but synthetic rubies. They were first founded in 1923, mixing alunbra and chromium pigments. In this way precious stones are obtained very similar to natural ones, both chemical and physically. However, the use of synthetic blond is greater in watchmaking than in jewellery.
Sapphire is as hard as ruby. It is usually found in mines rich in rutile, bauxitata and hematicity. It consists of a mixture of aluminum oxides, iron and titanium. Its color varies from light blue to dark blue, depending on the amount of titanium, the blue is lighter or darker. Its hardness on the Mohs scale is 9, a degree less than the diamond.
The main producers of Zafiro are in Africa, but in recent years several mines have been found in South America. It is used especially in jewellery and in various applications of lasers. Formerly it was thought that this stone kept wisdom, that is, that the person who had a sapphire was a person of great wisdom.

Beryllium is the basic component of the emerald. It also has chromium and vanadium atoms, among others. It is very rare to find quality emeralds with more than one kilate. In fact, the larger ones often present visible impurities. The emerald has been produced for more than 3,000 years.
Ancient art
Despite its beauty, precious stones shine brightly carved, and its cultivation is not something current. Since time immemorial, the materials are sawn, cut, perforate, give shape and finally pulen. Over time, stone builders have developed various techniques and processes to optimize the beauty of these beautiful materials.
In prehistory, basic steps were also taken to work the stones. Although it seems a lie, these steps were technically quite advanced. For example, to shape the material, abrasive stones were used, then the stone was pressed with thinner abrasives and finally the burin was used to drill.

All these techniques were not intact and were gradually developed. The next challenge was to work on precious stones. That is, in these precious stones, various motifs began to be decorated.
The next innovation came approximately in the Middle Ages. In fact, the parts of the precious stones began to work perfectly. The aim was to highlight, so to speak, the brightness of the stone.
Today, stone farmers continue to use all these ancestral techniques, but, of course, with the new tooling. Among other things, they use computers for the design and laser beams to work precious stones.
As technology advances, little by little doubts about the composition and color of precious stones are resolved. Recently, for example, a group of researchers from the University of Córdoba has developed a method to determine in a few minutes the chemical composition of jewelry. In fact, nowadays there are several methods to know the composition of jewelry, but they are long and, sometimes, destructive processes. The method developed in Córdoba, in addition to fast, is reliable and does not destroy the strange thing. X-ray fluorescence is the method of analysis of metals and their concentration. The device looks like a scanner. It is also an environmentally clean method by not using contaminating products.
It is interesting to know the composition of precious stones, since often the composition and color are related. More specifically, depending on the impurities that appear, it is believed that the gem acquires one color or another.
Red and green

The color indicates the leap that the electrons of an atom must make to pass from the fundamental state to the excited state. In this case, chromium is the one that gives color to precious stones. All the chromed compounds are coloured.
Each chromium ion is surrounded by six oxygen atoms, both in the crystalline structure of the blonde and emerald.
In addition, until now, it was thought that color was largely provided by neighboring atoms. Therefore, the blonde and the emerald should have the same color, since the adjoining atom is the oxygen in both. But it is not so.
In 1957 L.E.Orgela stated that the distance between chromium and oxygen atoms is different in these precious stones and therefore have a different color. But this explanation did not convince many experts. In fact, precious stones are hard materials that saw it impossible for the distances between atoms to be so different. In fact, in the 1980s, using a technique developed to measure the impurities of precious stones, French researchers discovered that the distance between ruby and the atoms of emerald is the same.

Recently, after several calculations, a group of physicists from the University of Cantabria has found an answer. For this purpose they had to use the concept of electric field. Because if you think that precious stones are crystal solid without activity, you are wrong. Electrons move constantly and lose and gain energy between energy levels.
In these energy fluctuations, in both cases the purple blue light of the spectrum is absorbed, but in the case of the emerald the red light is also absorbed. Therefore, it remains green. That is why the emerald is green. In Errubia, for its part, the green light is absorbed, to which it owes its red color.
Although this secret has been hidden for a long time, in the end they have revealed it. However, precious stones have not lost their natural fascination, and researchers will continue to discover the hidden aspects of these precious and expensive jewelry.





