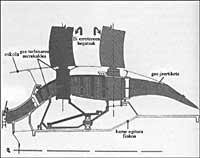
Space plane
1988/12/01 Otaolaurretxi, Jon Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria
One of the biggest obstacles is in propulsion, so we are working and researching in different forms of propulsion. Cryogenic propulsion is not yet well mastered and the materials to be used must withstand high temperatures. Therefore, metal materials and composites should be used. On the other hand, they should also investigate aerodynamics, combustion, design, mechanics, etc.
But first of all we have to define what the space plane is. And this type of plane, with its own means, will have to take off, land as a satellite.
The American NASP project is similar in Europe; in the German Federal Republic (SÄNGER), Great Britain (HOTOL) and France (STS). In some projects the space plane is two-part (which loses part in propulsion) and in others one-part.
On the other hand, we must take into account the similarity between the space plane and the hysonic plane that the Earth can perform semipoically. Although they may be different architectures, they resemble propulsion. In the propulsion of the planes that will take off and land horizontally will have much to see the following factors:
- Travel characteristics (height and speeds): The height would range from 0 to 100 km and the speed between 0 and 25 Males. 1 Mach = speed of sound propagation in the air.
- Type of plane (partial or double) and dimensions.
- Acceleration levels allowed.
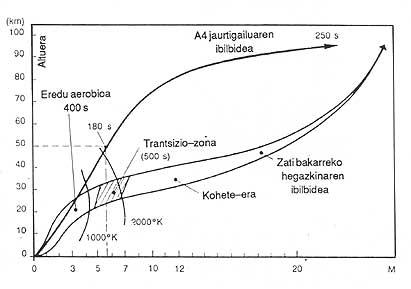
The types of engines that can be used in propulsion are different: turboreactor, statorreactor and rocket. Each motor has its advantages at certain speeds.
Turboreactors
for example, up to 4 Machs, stationary reactors between 2 and 7 Mach, and rocket reactors between 0 and 25 Mach are used. From these stops, the entry temperature to the turbine would go from the current 1.850K to 2000K.
The turboreactor has the advantage of burning little. That is why the specific impulse is usually from 4,000 to 10,000 seconds. The specific impulse indicates the second in which a kilogram of fuel exerts a kilogram force.
However, turboreactors can only be used up to 4 Males, unless the inlet air cools, but this pathway is complicated and heavy and improvements would be up to 4.5 Machs.
Another system consists of combining turboreactor and rocket. The exhaust gases from the rocket engine would enter the turbine and thus obtain 5.5 Mach, but the specific impulse would drop to 2,000 seconds.
Statorreactors
They are very simple motors, as they have no moving parts. However, at low speeds they cannot be used and do not serve to take off the plane from the ground. The specific impulse is good (more than 4,000 seconds), but the speed has its limit around the 7 Mach.

Aerobic rocket engines,
uses air as an oxidizer in the atmosphere. This air cools and compresses.
Therefore, the combination of these three types of propulsion described is currently being investigated. A combination may be the turbo-statorreactor rocket, but turbo-statorreakote rocket combinations are also studied.
The fuel of these engines is also important. The difference between kerosene and liquid hydrogen is 11 to 1 in density and 1 to 2.5 in calorific value respectively. Methane also has its importance as fuel. It is easier to handle than liquid hydrogen.
However, although the space plane that will reach 30,000 km/h is still an empty project, we hope that we know it made reality before time.

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia