Hubble: 10 years looking at space
2000/11/01 Arregi Bengoa, Jesus Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria
Planets
It has taken accurate images of the planet of our system and what happened in it. The highlight was the continuation of the collision of comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 fallen to Jupiter in 1994.
Stars
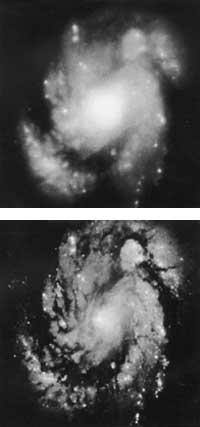
Hubble analyzes the processes of creation and death of stars. It has confirmed the existence of a disc of rock and dust around the emerging star. Just as Earth or Jupiter emerged, planets are created on this disc. In the case of dying stars planetary nebulae have been seen. These nebulae are the large shells of matter that the star creates around it.
It has also been possible to observe supernovae. In particular, the traces of what happened in 1987 have been observed. The observation dates from 1994, that is, images have been taken of the phenomena derived from the event.
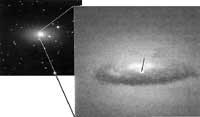
Black holes have also been investigated through Hubble. They have been studied mainly in the nuclei of galaxies. In theory it was thought that there could be a giant black hole in our core. This theory has been confirmed in some external galaxies. The observation of the nucleus of our galaxy is impossible because of the large amount of gas involved and that this is a great drawback.
Galaxies
In addition to the black holes mentioned, other characteristics of galaxies have been analyzed through Hubble. Many quasars have been found. Quasars are considered very active galaxies. Those found are far away. Therefore, such observations require a high-resolution telescope.
Universe Age
Observations made through Hubble serve to determine the age of the universe. Two working groups have participated in this work, using two different methodologies. One of them has used supernovae type 1A, while the other has used special stars called cefeidas. Since data sources and treatments were different, different results have been obtained. However, the difference is not that big. Moreover, it seems that despite previous opinions, the universe is expanding faster and faster.
Once this is considered, they have had to perform the calculations again. The new value of the Hubble constant has been obtained and age has been calculated. A group has aged 13.5 billion years. The other, however, was 15.5 billion years. The difference between the two, 2.5 billion years, is an inferiority, less than 10%.

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia