Hard ice and organic molecules, among the first results of Philae
2014/11/19 Galarraga Aiestaran, Ana - Elhuyar Zientzia Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria
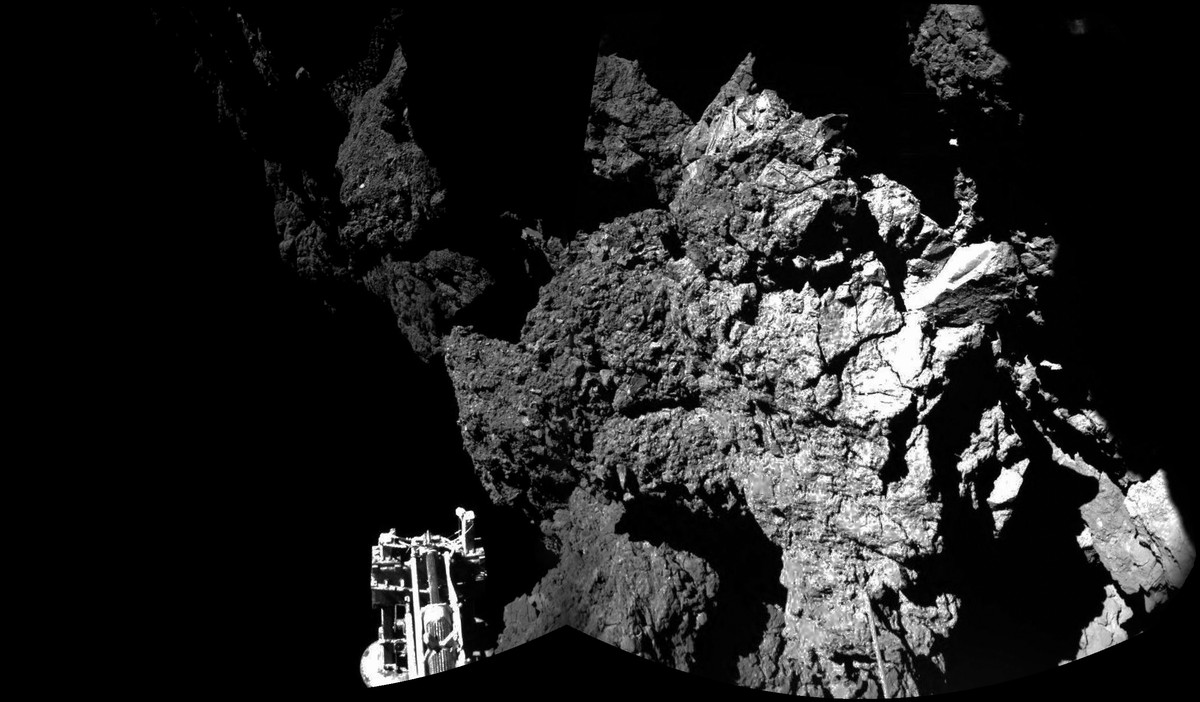
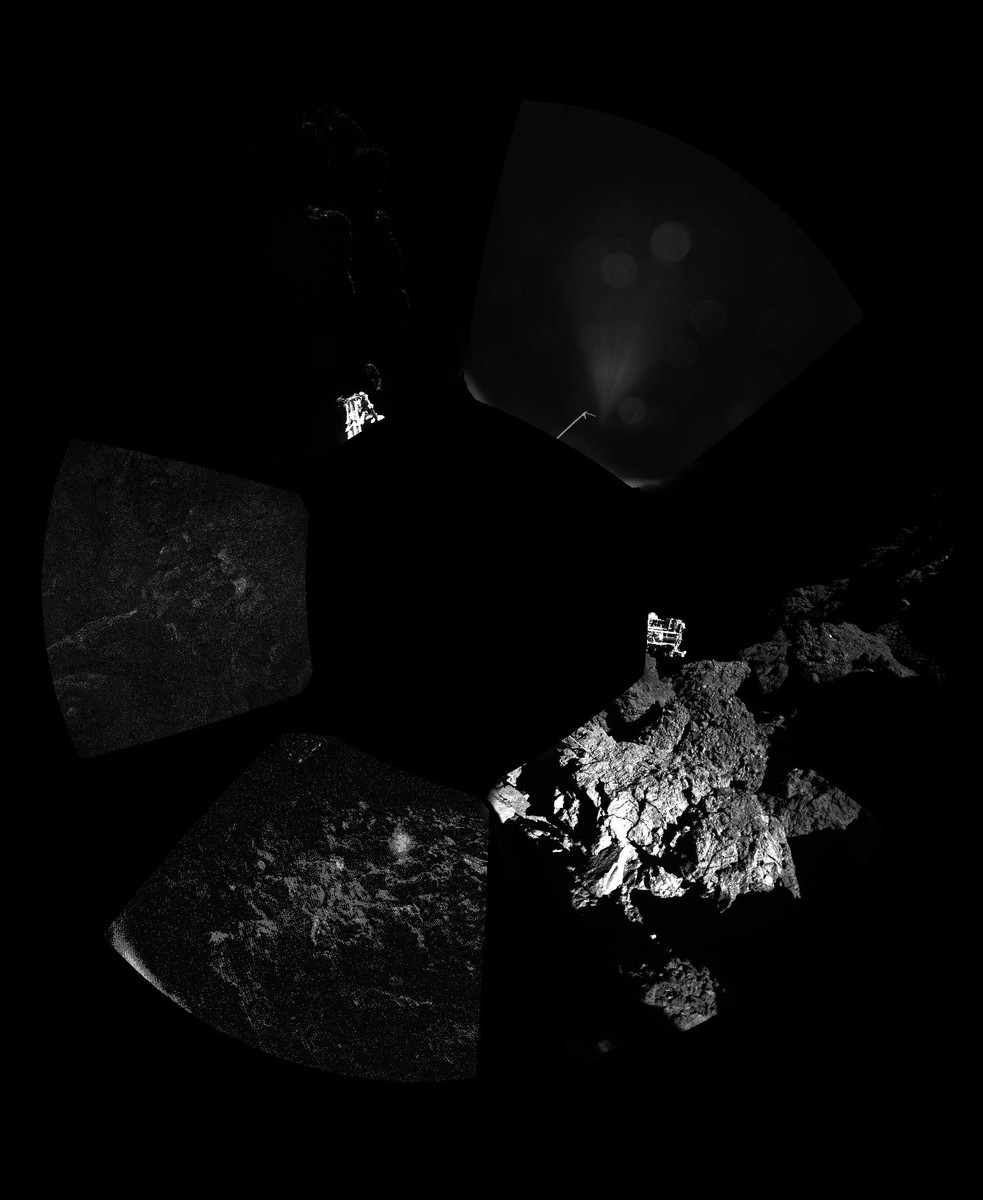
However, the first results were still in progress. These are images taken by the CIVA camera, according to which the surface of the comet is rocky and abrupt, and is covered with dust.
Now, thanks to MUPUS, they have discovered that this layer of dust is 10 to 20 centimeters thick and have received a surprise: under there is ice and it is very hard. The researchers did not expect the ice to have a structure similar to snow or chalk. It seems not like this: the drill has not been able to cross the ice and the SESAME tool has confirmed its hardness. Likewise, the data sent by SESAME suggest that the activity of the area in which Philae is located is reduced.
COSAC and PTOLEMY can also surprise. Their mission is to detect and identify the molecular ones, and check if their quirality coincides with that of Earth's molecules. Although the data collected is still being analyzed, it seems that there are organic molecules in the coma, so it is possible that results are soon even more significant.
Together with them, the results of the measurements obtained by other instruments will be communicated. Among them, those of ROMAP. Among other responsibilities, he had to analyze the magnetic field of the comet and, although it seems paradoxical, the emission of two boats by Phila has helped in his task by measuring a wider field than planned thanks to the boats.
In addition, those of the ESA do not rule out the possibility of resuming Philae when it approaches the Sun more and has more light. Therefore, there is no doubt that, despite the difficulties, the congregation of Philae has been a success.

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia