Have detected liquid water on Mars, a large lake under ice
2018/07/25 Etxebeste Aduriz, Egoitz - Elhuyar Zientzia Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria
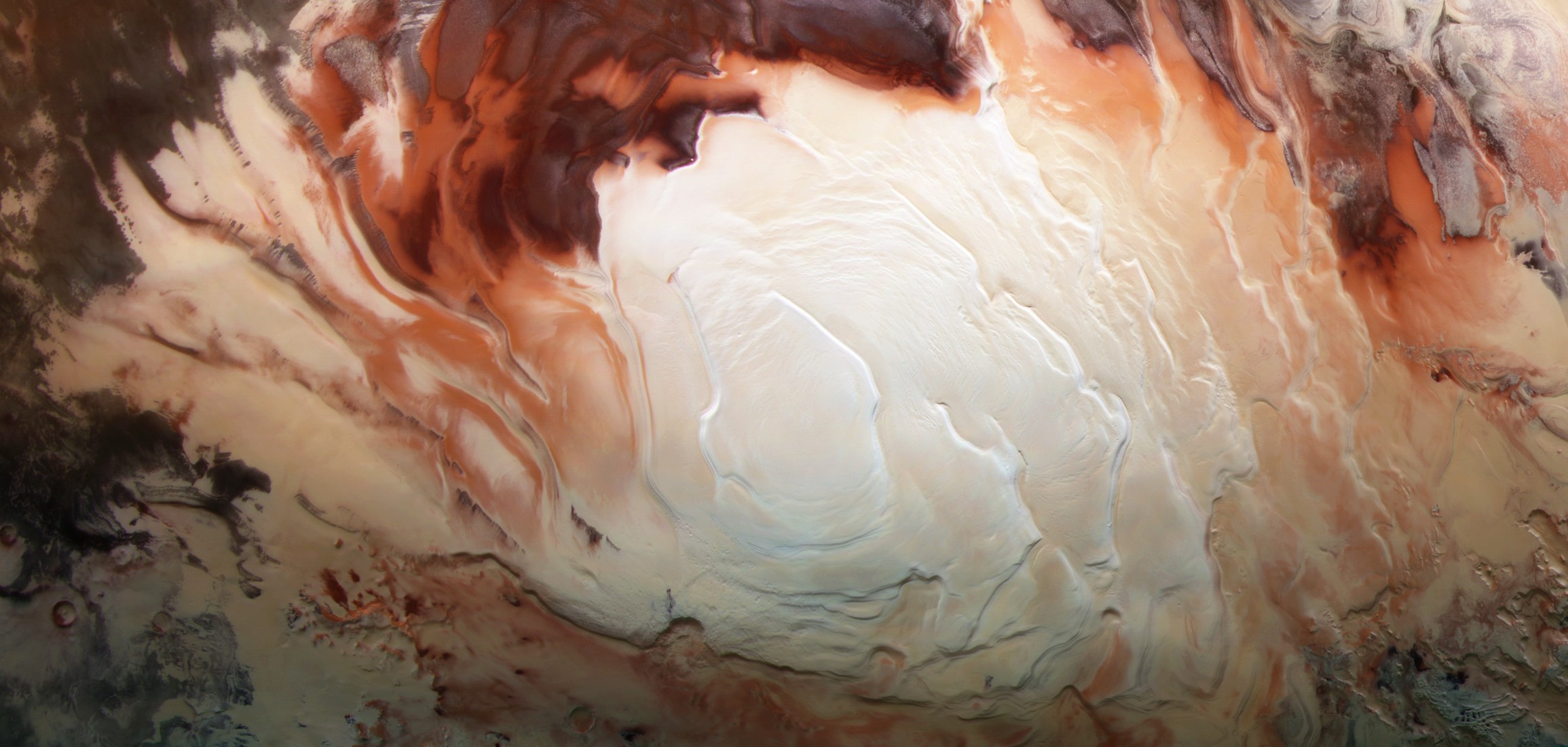
A group of Italian researchers announces that they have detected a large lake under the ice on Mars. Discovered in the South Pole, 1.5 km deep under ice, the lake has an approximate width of 20 km. The finding has been announced in the journal Science.
_display_home.jpg)
Although under the polar ice hulls liquid waters were suspected, so far they have not been found. They have now found the MARSIS radar on the Mars Express probe. Between 2012 and 2015, after analyzing several measurements made by the radar in the area called Planum Australe, it is observed that under the ice layer of kilometer and a half the radar signal changes sharply. And the profiles provided by the radar in this area are very similar to those of the underwater lakes located in Antarctica and Greenland. Thus, they conclude that on Mars there is also a lake under the ice.
Researchers believe that the water temperature of this lake is lower than the freezing temperature of the water. Because magnesium, calcium and sodium are common on the surface of Mars, it would not be strange that their salts were dissolved in water, so the pressure of the ice sheet would decrease the freezing point of the water.
“The existence of a large lake on Mars is important news, and opens up the possibility that in other places on the planet, below the surface, there are other lagoons at a lower depth”, explains Agustín Sánchez Lavega, director of the Group of Planetary Sciences of the UPV. “And if there is liquid water, being one of the essential components of life, the chances of finding life on Mars increase considerably.”




