Against cavities, best saliva
2011/11/01 Urruzola Arrate, Manex - Elhuyar Zientziaren Komunikazioa Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria
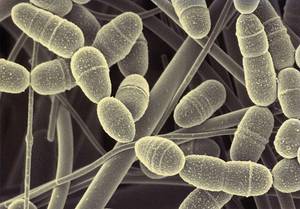
The mouth is the scenario. The protagonist actor is a bacterium. It's called Streptococcus mutans and likes sugar, in fact it doesn't eat anymore.
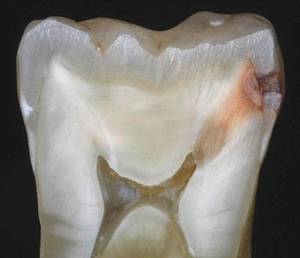
The scene begins after a meal: the bacterium searches for carbohydrates in the mouth, in the remains of foods that have remained between the teeth and feeds on the sugars it finds. Then the bacterium makes digestion and during it produces acids. These acids are the ones that damage the scenario, that is, they damage the enamel of the teeth and create cavities.
The fundamental ingredients for the development of the caries scene are, therefore, at least two: bacteria and carbohydrates present in food. But the duration of the event is also decisive: Streptococcus mutans takes more than 24 hours to metabolize food and form acids. Therefore, the function can be interrupted if the protagonist's activity is interrupted. That is, if Streptococcus mutans is prevented from working 24 hours in a row, jokes will not appear.
Better brush than pasta
Obviously, one of the ways to hinder the activity of bacteria is to clean the teeth properly and frequently. The key to good dental cleaning is to brush well. In fact, it is important to remove the bacterial plaque well with the toothbrush and not so much toothpaste. According to Julian Aguirrezabal dentist, toothpaste, in addition to giving a pleasant flavor, does not serve much. Consider it a chap: "Toothpaste does not have the function of detergent as it is believed. Even without pasta the teeth can be washed perfectly, but we are exposed to seeing the shields that appear on the teeth in television ads," says Aguirrezabal. Txemi Errazkin, president of the Gipuzkoa College of Dentists, underlines the need for brushing: "We must remove dirt, clean it with mechanical work. It is better to brush your teeth well, although only with water," says Errazkin.
Without detergent function, dental pastes have bactericides. That is, in the pasta there are substances capable of killing and eliminating bacteria. However, both physicians remain important to the bactericidal effect of dental pastes. "It is necessary to remove the bacterial plaque against cavities, not kill bacteria," says Errazkin. According to Aguirrezabal, "bactericides containing dental pastes do not serve much, since bacteria are immediately regenerated in the mouth".

External effect of fluoride
The most beneficial and well-known component of toothpaste is fluoride. Fluoride is one of the main protectors against caries: it makes the enamel that protects the teeth more resistant to the degradation of acids.
Beyond the fluorine present in toothpaste, it is known that the fluid that enters the water supply reduces the number of cavities of the inhabitants of the area. For this reason, for years it has been believed that fluorine had a systemic effect, that is, when drunk, it was placed in the body and hardened the teeth with blood. However, according to studies of recent years, the greatest influence of fluoride is the topic: in the mouth, fluoride comes into contact with the outer layer of the tooth and the teeth harden. "We now know that the systemic effect of fluoride is almost inappreciable; the greatest effect of fluoride is local," says Errazkin. Therefore, it makes no sense that pregnant women receive fluorinated supplements to benefit their teeth.
Fluoride can be ingested in various ways, such as drinking along with tap water or taking additional pills. However, the most effective ways to take fluoride are those that come into contact with the teeth: paste, gel, varnish or fluorinated collutories. However, the influence of fluoride is much more pronounced in children than in adults. In fact, "you can influence the enamel of the teeth that are forming or that are of new creation, but the enamel of the teeth of the adults is already cured and there it is more difficult to provoke changes", explains Aguirre. "The fluoride of toothpaste favours children, but it is more difficult to influence adults. That's why I would recommend choosing the pasta that you like the most, apart from advertising," adds Aguirrezabal.
Importance of saliva
However, brushing and fluorine are not the most decisive protective measures against caries. One of the most important factors affecting cavities, if not the most important, is saliva. The 99% of the saliva is water, but the remaining 1% has antimicrobial components and acid neutralization capacity. It is, therefore, an excellent recipe against cavities. "To have a healthy mouth, the most important thing is that saliva flows abundantly," says Aguirrezabal.
It is rare that people's saliva lacks any element, but sometimes the amount of saliva is reduced, which causes problems. As Aguirrezabal warns, "the decrease in saliva causes the drying of the mouth, and the dry mouth is a nursery of cavities." What prevents the abundance of saliva? Aguirrezabal has his answer clear: "There are diseases that prevent salivation, such as Sjögren syndrome and diabetes, but they are mostly drugs. There are more than 400 drugs in our market that reduce salivation, such as antidepressants."
Another aspect to take into account for saliva is that it flows only day and not night. In times of sleep, therefore, the mouth does not produce anti-drug and is left with less protection. "That's why we recommend brushing your teeth before bedtime," recalls Aguirrezabal.
Collutories and xylitol
When saliva cannot work properly, or when there are too many bacteria in the mouth, prepared antimicrobials can be used. These substances carry out an intense bactericidal work that helps to reduce the number of bacteria present in the mouth. In this way, to some extent, they help protect the teeth against cavities.
Chlorhexidine is one of the best known antimicrobial agents and is marketed as a collusion or oral rinsing solution. But a prolonged intake of chlorhexidine can cause a dyeing of the teeth and a decrease in taste. In addition, at first it is effective to kill bacteria, but with time the bucal flora gets used and loses effectiveness. "Collutories are effective if used in the short term, but it is not convenient to use them for more than three consecutive weeks," explains Errazkin.
Xylitol is another effective antimicrobial agent. This substance is as tasty as sugar, but has the ability to protect it from cavities. This is based on its effectiveness: In his ability to deceive Streptococcus mutans. As xylitol has sugar flavor, the bacteria eat it. But it cannot be metabolized, since xylitol is a polyhydric alcohol. Therefore, when the bacterium eats xylitol, it is created an ingestion that cannot form acid. Hence its use in anticaries treatments.
Chicles with xylitol are also sold. But not everything is gold. In fact, xylitol is a very expensive substance and in many products a minimum amount is introduced to predict that it contains xylitol. "It's a marketing," says Aguirrezabal. "According to a study by the University of Washington, a minimum of six grams of xylitol per day would be needed to protect against cavities."
Contagious disease?
However, caries is a common disease. In fact, it is the most frequent disease that children suffer. "In general, in young people, caries disease is more widespread, and the more adult, the less caries it is," explains Errazkin. With age the pH of saliva and mouth is changing. And the bacterium that produces the caries Streptococcus mutans is changed the most suitable place of life. Therefore, the bacteria that have not disappeared but that produce cavities decrease over the years.

In addition to being normal, the debate about whether caries is contagious is now very fashionable. "Research indicates that Streptococcus mutans passes from parents to children," says Aguirrezabal. "Therefore, at one time it was thought to be a hereditary disease because it passed from parents to children. But it's more complex than that," he adds. In fact, caries is a multifactorial disease, and the presence of the bacterium Streptococcus mutans in the mouth does not necessarily imply the development of caries. According to Txemi Errazkin, "there is no strong scientific evidence that caries is contagious. The transmission of bacteria is constant: from the feed of the mother to the child, in the kisses... but that does not mean that the disease is transmitted. In the body we have thousands of bacteria. But one thing is to have bacteria and another to develop the disease."
But beyond transmissions, cavities still have other issues to clarify. For example, why does it happen that a tooth is totally eaten of cavities, but that the tooth next to it has no joke? This phenomenon is known as local immunity. "Each tooth has its own immune system around it," says Errazkin. "This is the case, but the underlying reasons are unknown at the moment." As seen, caries is a complex disease that, in addition to being common and infectious, has many agents.