Z-machine
2006/03/09 Roa Zubia, Guillermo - Elhuyar Zientzia
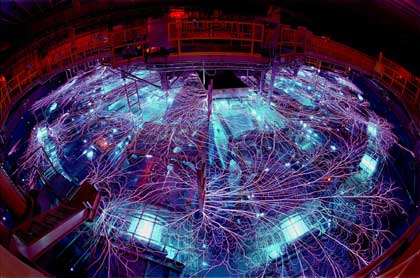
The American laboratory Sandia has created a plasma of two billion degrees of temperature, a temperature higher than that of the interior of the stars. This high temperature has been achieved through the Z machine, which transforms metal threads into plasma. In experiments that are now
recent, wolfram threads have been used instead of traditional steel threads, which are thinner, and have discovered that tungsten is an ideal metal for making plasmas. The high-intensity electric current passes through the wire and the metal atoms of the wires are ionized and the solid becomes gas. In short, they get a plasma, that is, a fluid of charged particles. Plasmas are controlled by magnetic fields, which in this case have used the magnetic field to physically compress the plasma, give speed and stop it abruptly. As a result, they have achieved a plasma at high temperature, a plasma at two billion degrees, to which the plasma
emits X-rays by itself. In addition, it releases four times more energy from the absorbed. Therefore, physicists have considered the experiment important, which shows that the Z machine can be used to investigate processes of fusion, high radiation, stellar flames, etc. The photo
shows the Z machine. (Photographer: Randy Montoya)




